Migrating relational databases to PostgreSQL using EuroDB tools
A lot of applications allow the use of different database engines. It is therefore possible that the decision to choose a particular engine was made too hastily or the requirements for the application itself have changed. An important recommendation to change the engine may also be the high license costs of the existing database solution. In these cases, database migration becomes the best solution. Today we will introduce the topic of migration, its security and simplicity – using the solutions offered by the tools from EuroDB.
A lot of applications allow the use of different database engines. It is therefore possible that the decision to choose a particular engine was made too hastily or the requirements for the application itself have changed. An important recommendation to change the engine may also be the high license costs of the existing database solution. In these cases, database migration becomes the best solution. Today we will introduce the topic of migration, its security and simplicity – using the solutions offered by the tools from EuroDB.
Before we begin our considerations concerning migration, let us first explain in a brief summary what migration is and what opportunities it offers. Database migration is a lossless transfer of the database schema with all its data to another database engine. Thanks to migration, we are able to make the database available for any required application (which allows faster data propagation), open up to cloud solutions or save money by choosing a cheaper alternative.
Is migration safe?
Data migration is one of the biggest IT projects. It is therefore important to ensure that it is carried out correctly and that the data remains intact. The question then arises as to whether migration is a safe process. The answer depends on many factors. One of them is the type of database from and to which the migration will be carried out. Another is the complexity of the data. The security of database migration, i.e. whether it will be possible to change the engine without losing the structure or data, is therefore directly dependent on the complexity of the database. In order to maximise security and properly prepare for migration, it is worth making a backup copy of the database (as described in the previous article). This will ensure that the original database remains intact in the event of a failure.
Migration capability limitations
It should be emphasised that database migration has its limitations and depends on the data organisation structures used. The most common type of databases used in IT are relational databases (RDB). Programs for their management are called Relational Database Management Systems. They are specific engines by means of which the database is built. The most commonly known RDBMS-s are:
- PostgreSQL – free, stable and constantly developed management system. Good for solutions such as Enterprise, but lacking technical support.
- EuroDB – an extended, fully supported PostgreSQL-based database platform with many additional modules to expand PostgreSQL standard capabilities
- SQLite – free and portable. Ideal for storing the database for desktop applications
- MySQL – free and easy to learn. Good for the start of the company
- Microsoft Access – Microsoft’s response to the simplicity of MySQL with an additional graphical interface
- Microsoft SQL Server – Microsoft’s response to the Enterprise solution
- Oracle DB – Oracle Corporation’s response to the Enterprise solution.
In an ideal world, any existing engine based on a relational database would allow for easy migration to another engine. Unfortunately, it has long been known that some paid RDBMS-s are so closed that the traditional tools used for migration do not provide 100% certainty that all data will be transferred correctly.
Is there a cheap, easy, and secure way to migrate to PostgreSQL?
Numerous companies offer the possibility of migrating the database to another database engine. Although this service is usually not cheap, for a person not familiar with databases and wanting to keep all their data it might seem to be the only option. However, it turns out that in the case of simple databases, the problem becomes relatively easy to solve. Some popular RDBMS-s include built-in migration modules that allow a smooth transition from one engine to another. In the case of migration of more extensive databases, however, such built-in modules are usually not enough. Not all data is migrated and in the database are created errors. Then you need to use special tools. One such tool is a module for migrating data from the EuroDB package. This module has been designed with security and simplicity in mind when migrating from the most popular databases, such as SQLite, MySQL or MS SQL.
Example of migration from SQLite using EuroDB tools
To demonstrate the simplicity of migration using a module from the EuroDB toolkit, we will present an example of migrating a simple database created on the SQLite engine to EuroDB, the engine of which is Postgres.
The following procedure was created for the EuroDB 13 database and its default configuration. It will work for any PostgreSQL-based database. The commands for different database solutions may differ slightly as the paths to the configuration files depend on the name of the specific database.
In the example, we skip the installation of the tool, which is available with EuroDB, and its installation is very simple.
First, we log in to the Postgres console.
sudo -u postgres psqlThen we create a database in which the migrated data is to be stored. In our example it is called db_from_sqlite.
CREATE DATABASE db_from_sqlite;Next, make sure that the migration module has the ability to connect to the database. To check this, locate the pg_hba.conf file. The easiest method is to execute the following command in the Postgres console.
SHOW hba_file;Once the path to the pg_hba.conf file is known, we can edit it in order to establish a correct connection to the database.
host all all 0.0.0.0/32 trustNow all that remains is to execute the following command, which will take care of the entire migration process.
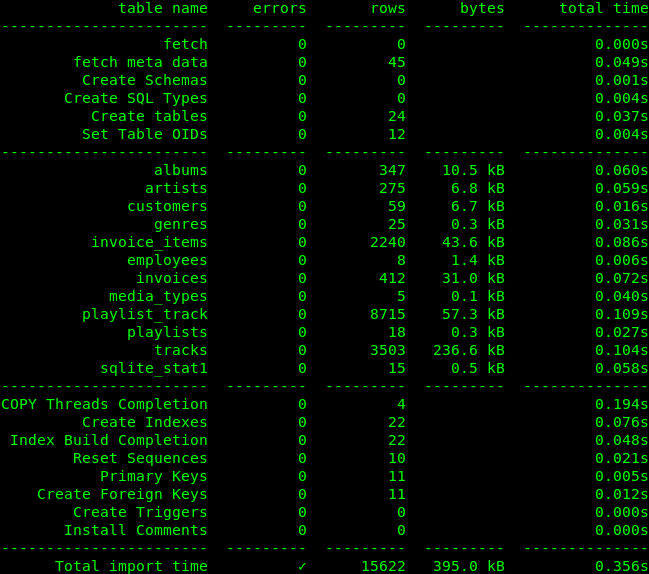
sudo eurotransfer /path/to/chinook.db pgsql://[email protected]/db_from_sqliteAfter the operation, the migration script returns a summary containing the migration details along with the number of possible errors that occurred. As you can see in the image below, the database migration was conducted without any problems, and the procedure itself was very easy.
Summary
With the database migration task ahead of you, you should be particularly careful and properly prepared for this task by creating backups. To make your task easier, you can use the migration module offered by the EuroDB toolkit. The module is easy to use, and thanks to its versatility, we can migrate databases from the most popular database engines to PostgreSQL. Therefore, it can be concluded that it is suitable both for people who start their adventure with databases, as well as for developed companies in order to increase the efficiency of migration.